Appyter Workflows for Analyzing Gene Sets with ChEA-KG
The ChEA-KG API has been extended to identify and analyze enriched regulatory subnetworks within two Appyter notebook workflows, which extend Jupyter notebooks to create functional standalone web-based applications. Read more about and try out each Appyter below.
ChEA-KG Appyter
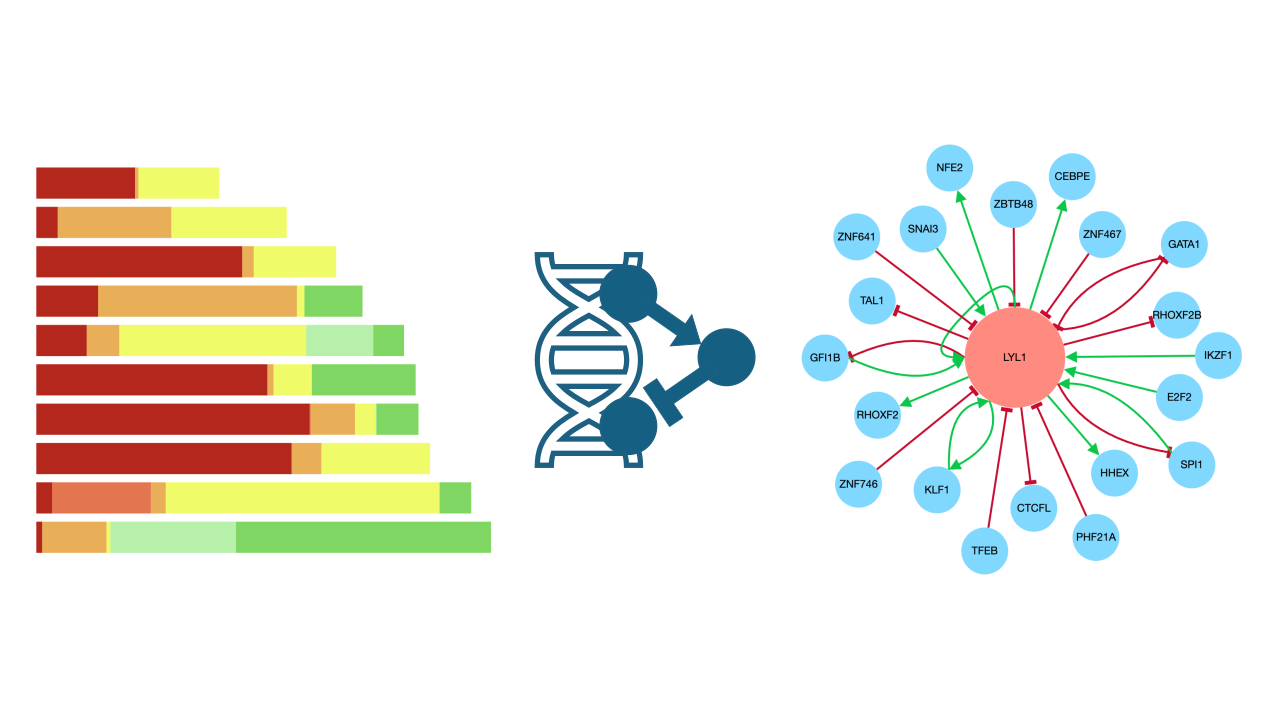
The ChEA-KG Appyter predicts regulatory subnetworks of transcription factors (TFs) for an input gene set. The query gene sets are compared against libaries of TF target gene sets in ChEA3 to identify the most likely regulating TFs. The TFs are then connected via edges in the ChEA-KG background gene regulatory network (GRN). This network was constructed by submitting thousands of gene expression signatures from RummaGEO to ChEA3 for transcription factor enrichment analysis. The functions of enriched TFs are predicted using the Gene Set Foundation Model.
ChEA-KG-TS Appyter
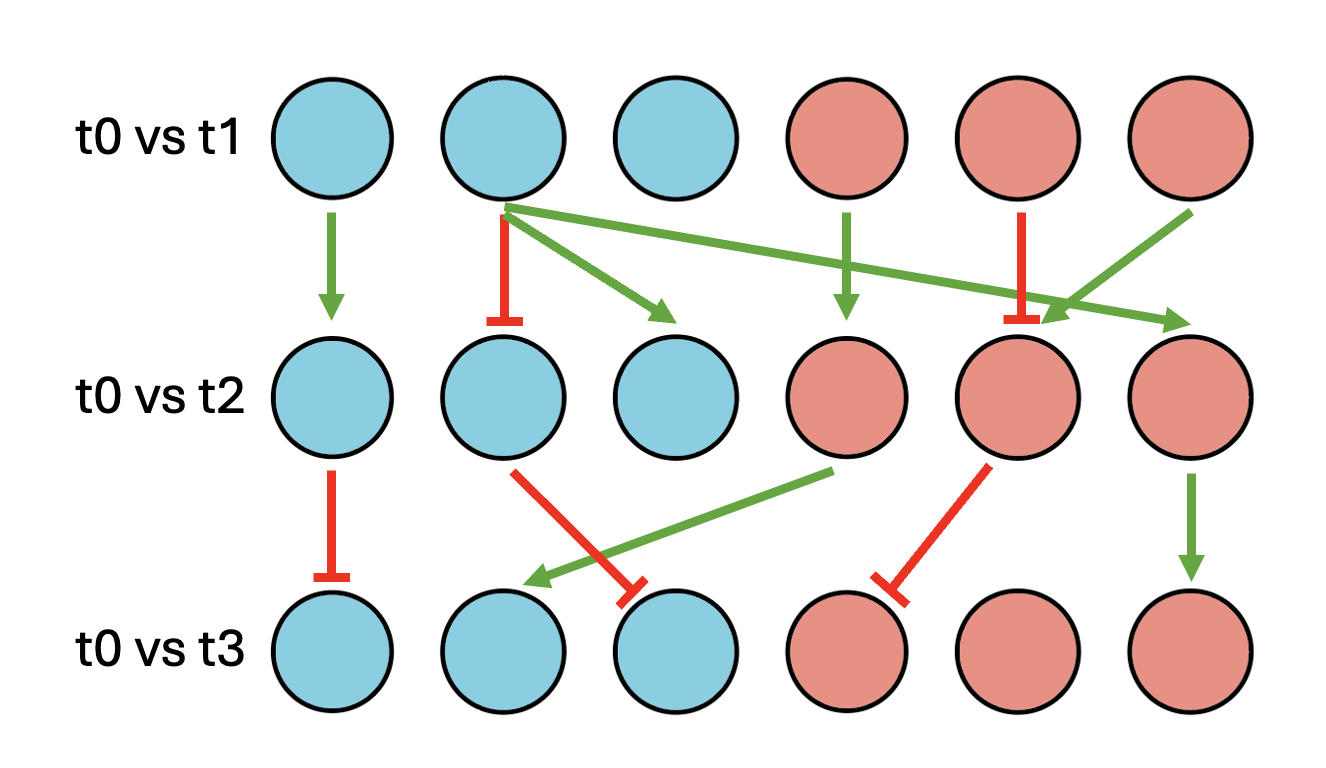
The ChEA-KG Time Series Appyter visualizes the enriched transcription factor landscape from time series RNA-seq data, helping to inform hypothesis about the regulatory mechanisms governing biological processes.

